Inflation in Europe has undergone significant changes in recent years, with rates peaking in 2022 and gradually declining since then. Understanding these trends is crucial for individuals and businesses alike, as inflation impacts purchasing power, savings, and investment decisions.
Current Inflation Landscape
As of April 2025, the euroarea’s annual inflation rate stands at 2.2%, aligning closely with the European Central Bank’s (ECB) target of 2%. This marks a significant decrease from the highs observed in 2022, when inflation reached 8.4%.
The decline in inflation can be attributed to several factors:
- Energy Prices: A stabilization and, in some cases, reduction in energy prices have eased cost pressures.
- Supply Chain Improvements: Post-pandemic recovery has led to smoother supply chains, reducing bottlenecks and associated costs.
- Monetary Policy: The ECB has implemented a series of interest rate hikes since mid-2022, aiming to curb inflation.
Central Bank Responses
The ECB has been proactive in addressing inflation. Since June 2022, it has raised its benchmark interest rate multiple times, reaching 2.25% by April 2025. However, recent statements suggest a cautious approach moving forward, balancing the need to control inflation without stifling economic growth.
In contrast, the Bank of England reduced its interest rate to 4.25% in May 2025, responding to slowing inflation and economic uncertainties. Similarly, the Czech National Bank cut its key rate to 3.5% as inflation dropped more than expected.
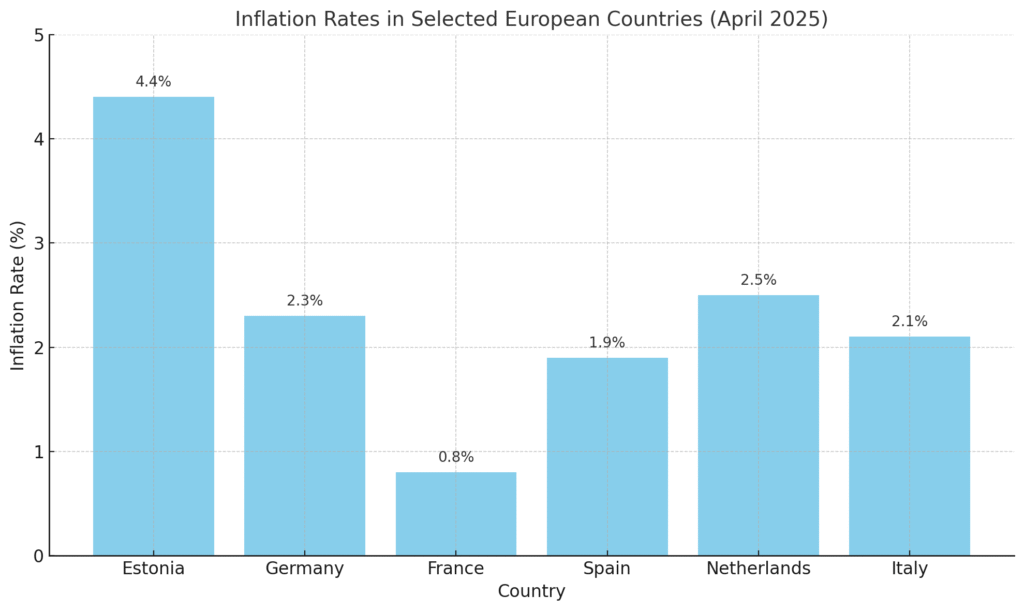
Regional Variations
Inflation rates vary across European countries:
- Estonia: Reported the highest inflation in April 2025 at 4.4%.
- France: Experienced the lowest rate at 0.8%, reflecting differing economic conditions and policy responses.
These disparities highlight the importance of localized strategies in addressing inflationary pressures.
Implications for Consumers and Investors
For Consumers:
- Purchasing Power: Moderate inflation helps maintain the value of money, but consumers should remain vigilant about price changes in essential goods and services.
- Savings: Interest rates on savings accounts may improve, offering better returns.
For Investors:
- Bond Markets: Rising interest rates can lead to lower bond prices, affecting fixed-income portfolios.
- Stock Markets: Companies with strong pricing power may perform better in an inflationary environment.
Looking Ahead
While inflation in Europe is trending downward, uncertainties remain:
- Global Trade Tensions: Ongoing trade disputes could disrupt supply chains and affect prices.
- Energy Markets: Geopolitical events may lead to volatility in energy prices, influencing overall inflation.
- Policy Decisions: Central banks must balance inflation control with supporting economic growth, requiring careful policy calibration.
Conclusion
Understanding inflation trends is essential for making informed financial decisions. As Europe navigates the post-pandemic economic landscape, staying informed about inflation and its implications will help individuals and businesses adapt effectively.
FAQ: European Inflation Trends
Euro area inflation stood at approximately 2.2% in May 2025, a slight easing from 2.4% in April
Core inflation remains elevated, particularly in services. Recent drops in energy prices and moderated goods inflation are helping bring headline rates closer to target
Consumer expectations for inflation over the next 12 months hovered around 3.1% in April, the lowest since 2021, while longer-term expectations (3-5 years) remain near target (2.1-2.5%)
Housing-related inflation remains high (around 6-7%), while food prices have risen over 4%, pressuring household budgets
With inflation near or slightly above 2% and external risks like geopolitics and trade tensions, the ECB is expected to proceed cautiously. Future rate cuts are anticipated if inflation stays stable
Slightly elevated inflation means moderate increases in the cost of living. Prepare by budgeting for rising essentials like energy, groceries, and housing
No, rates vary: Central and Eastern European countries tend to experience higher inflation than the euro area average, driven by wage growth and local economic pressures

