As Europe navigates the complexities of 2025, understanding employment trends from a financial standpoint is crucial. This article delves into the current state of the European labor market, highlighting key developments, sectoral shifts, and the financial implications for policymakers and stakeholders.
Current Employment Landscape
Recent data indicates a resilient labor market across the European Union. According to Eurostat, the EU employment rate reached 75.8% in 2024, with notable variations among member states, ranging from 83.5% in the Netherlands to 67.1% in Italy.
The OECD reports that the euro area’s unemployment rate stood at 6.2% in February 2025, maintaining a stable position since April 2022 .
Sectoral Shifts and Financial Implications
The European labor market is experiencing significant sectoral transformations:
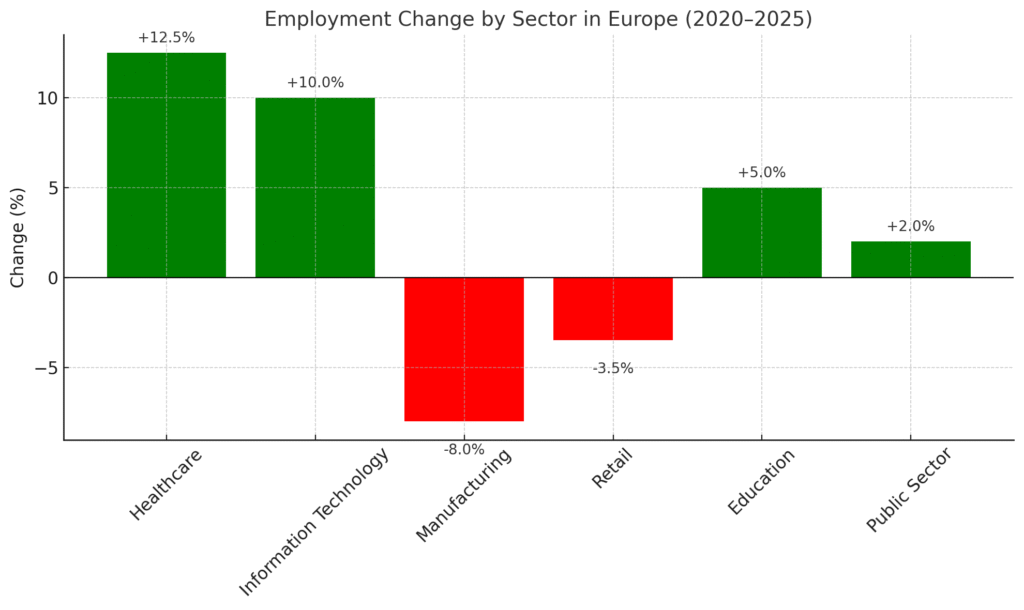
- Healthcare and Biotechnology: Driven by an aging population, healthcare spending in the EU is projected to exceed 10% of GDP by 2025, potentially creating up to 2 million new jobs in the sector.
- Manufacturing: Germany’s manufacturing sector has faced challenges, with a loss of approximately 250,000 jobs since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Factors such as high energy costs and global competition have contributed to this decline.
- Public Sector: In the UK, sectors like education and healthcare are experiencing hiring slowdowns due to government spending cuts and increased employment costs.
Demographic Influences
Demographic changes are reshaping the labor market
- Aging Population: The increasing proportion of older individuals in the workforce necessitates policies that support extended working lives and retraining opportunities.
- Migration: Foreign workers have become integral to the euro zone’s labor force growth, accounting for about half of the increase since the pandemic. Their participation has helped alleviate labor shortages and contributed to the growth of higher-skilled job sectors.
Wage Dynamics
Wage trends are influenced by various economic factors:
- Negotiated Wages: The European Central Bank’s wage tracker indicates that negotiated wage growth is expected to average 3.4% in 2025, a decrease from 4.6% in 2024. This decline reflects the fading impact of one-off payments and front-loaded wage increases from the previous year.
- Minimum Wage Policies: In the UK, recent increases in the national minimum and living wages have led to temporary pay rises. However, overall wage growth remains below historical averages, with businesses facing additional costs such as increased national insurance contributions.
Future Outlook
Projections suggest modest employment growth in the coming years:
- EU Employment Growth: CEDEFOP anticipates an annual employment growth rate of 0.4% at the EU level by 2035, influenced by the digital and green transitions alongside demographic challenges.
- Sectoral Opportunities: The healthcare sector is expected to continue expanding, while industries like manufacturing may require strategic interventions to address job losses and remain competitive.
Conclusion
The European labor market in 2025 is characterized by resilience amid economic and demographic shifts. Financial considerations, including wage dynamics and sectoral investments, play a pivotal role in shaping employment trends. Policymakers and stakeholders must remain vigilant, adapting strategies to support sustainable employment growth and address emerging challenges.
FAQ: Employment Trends in Europe
Europe’s employment rate has been steadily rising, with unemployment around 6%, and employment growth of about 2% annually in 2024
Tech and digital roles, healthcare, renewable energy, and green tech are leading with strong demand across the EU
Yes. many European countries face persistent shortages in skilled professions like ICT, healthcare, and manufacturing, amplified by demographic shifts and skill gaps
A shrinking labor pool due to aging populations (e.g., Germany, Italy, Poland) is prompting upskilling efforts and targeted recruitment for older workers
Remote and hybrid work has surged, and cross-border employment across the EU is increasing significantly, especially in tech and professional services
Active labor market policies, like training, job-placement programs, and reskilling, alongside EU funding (ESF+) have bolstered workforce participation and reduced unemployment
Wages remain elevated due to tight job markets, but narrowing corporate margins may force firms to reassess hiring and wage strategies
Key challenges include managing labor shortages, bridging skills gaps, demographic decline, and ensuring equitable access to quality jobs in a shifting and tech-driven economy

